World War II Map by Map

World War II stands as a pivotal moment in history, marked by its immense scale and impact. This war involved over 50 nations and resulted in an estimated 70 to 85 million deaths, reshaping global dynamics. The history of this conflict is vividly captured through maps that illustrate the vast scale and rapid movements of armies across diverse landscapes. These visual representations provide a deeper understanding of the war's magnitude and complexity, highlighting the significant civilian casualties, with about half of the European losses being non-combatants.
Prelude to War
Rise of Totalitarian Regimes
Germany and the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles imposed harsh penalties on Germany after World War I. The treaty demanded significant territorial losses and reparations. Economic hardship and national humiliation fueled resentment. Adolf Hitler capitalized on this discontent. He promised to restore Germany's power. His rise marked the beginning of a totalitarian regime.
Expansionist Policies in Europe
Totalitarian regimes in Europe pursued aggressive expansion. Italy under Mussolini sought to recreate the Roman Empire. Germany aimed to unite all German-speaking peoples. The annexation of Austria, known as the Anschluss, exemplified this ambition. Expansionist policies destabilized the region. Tensions escalated across Europe.
Early Conflicts and Alliances
Invasion of Poland
On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. This event marked the start of World War II. The invasion demonstrated the effectiveness of Blitzkrieg tactics. Rapid advances overwhelmed Polish defenses. The attack prompted Britain and France to declare war on Germany.
Formation of the Axis Powers
The Axis Powers formed through strategic alliances. Germany, Italy, and Japan shared expansionist goals. These nations signed the Tripartite Pact. The pact solidified their cooperation. The alliance posed a significant threat to global peace. The world braced for a widespread conflict.
The European Theater

Blitzkrieg and Western Europe
Fall of France
Germany launched a rapid attack on France in 1940. The German forces used blitzkrieg tactics to overwhelm French defenses. The speed and surprise of the attack led to a swift victory. German troops occupied Paris, marking a significant defeat for the Allies.
Battle of Britain
The Luftwaffe targeted Britain in a major air campaign. Germany aimed to destroy the British Royal Air Force. The battle involved intense aerial combat over British skies. Britain's defense proved resilient, preventing a German invasion. The victory boosted Allied morale and marked a turning point.
Eastern Front and Operation Barbarossa
Invasion of the Soviet Union
Germany initiated Operation Barbarossa in 1941. The invasion targeted the Soviet Union with massive force. German troops advanced deep into Soviet territory. The harsh winter and fierce Soviet resistance halted the advance. The failure marked a critical setback for Germany.
Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad began in 1941. German forces surrounded the city, cutting off supplies. The siege lasted for over two years, causing severe hardship. Soviet resilience and determination kept the city from falling. The siege ended in 1944, marking a symbolic Soviet victory.
The Pacific Theater
Pearl Harbor and American Entry
Attack on Pearl Harbor
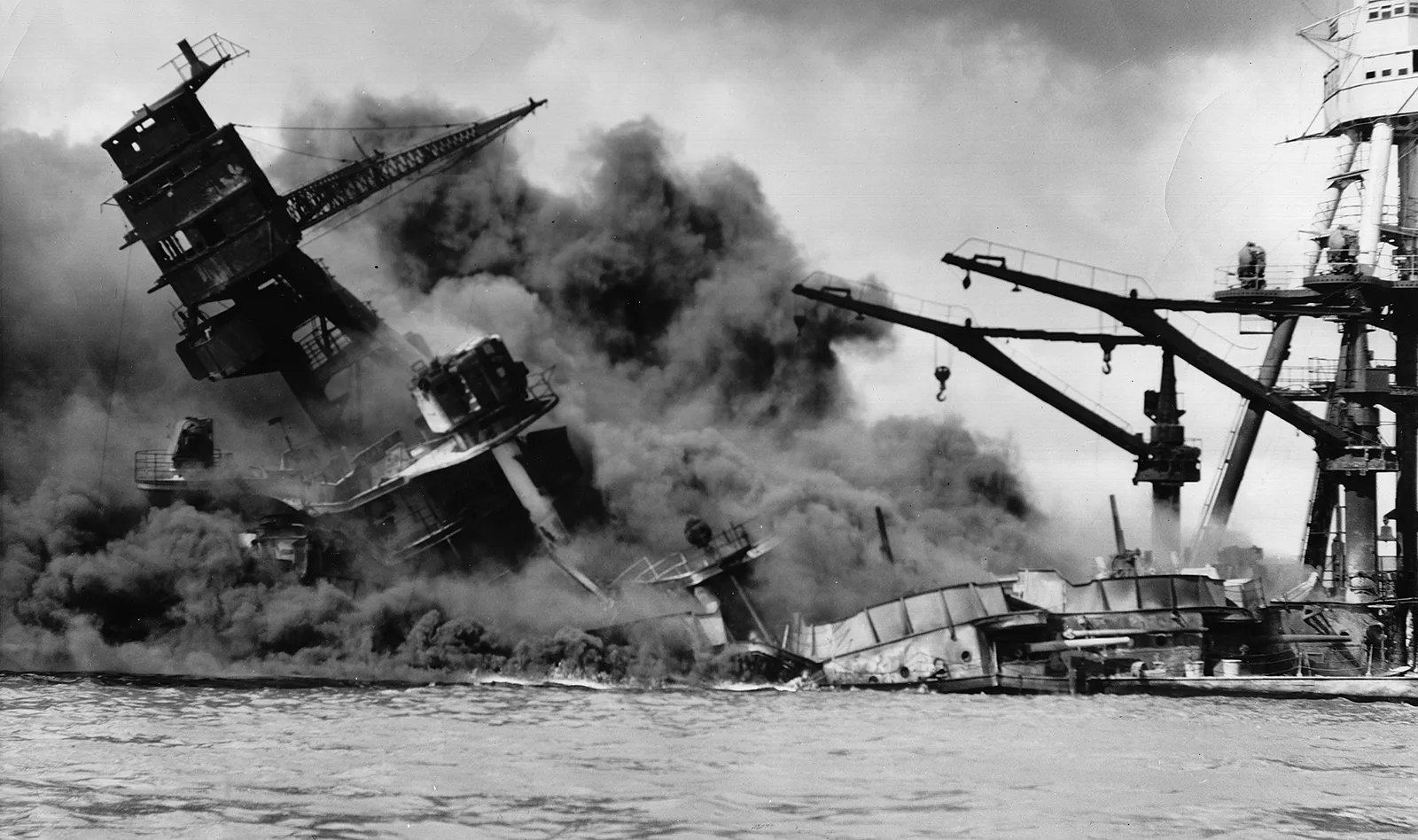

Japan launched a surprise attack on December 7, 1941. The target was the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor in Hawaii. Japanese forces aimed to cripple the U.S. Pacific Fleet. The attack resulted in significant damage and loss of life. This event prompted the United States to enter World War II.
U.S. Mobilization
The United States responded swiftly to the attack. Mobilization efforts began across the nation. Factories shifted from civilian to military production. The U.S. military expanded rapidly. American society united to support the war effort.
Island Hopping Campaign
Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway occurred in June 1942. The United States Navy faced the Japanese fleet. American forces achieved a decisive victory. The battle marked a turning point in the Pacific War. The Japanese fleet suffered devastating losses.
Guadalcanal Campaign
The Guadalcanal Campaign began in August 1942. American forces aimed to secure the island. The campaign involved intense jungle warfare. Control of Guadalcanal allowed the U.S. to begin leapfrogging throughout the South Pacific. The victory marked a significant step in the Allied strategy against Japan.
Forces Americas Armed Forces and Turning Points
North Africa and the Mediterranean
Battle of El Alamein
The Battle of El Alamein marked a significant turning point in World War II. British forces, led by General Bernard Montgomery, faced German troops under Erwin Rommel. The desert terrain challenged both sides. The Allied victory halted the Axis advance into Egypt. This success boosted morale across the Allied nations.
Invasion of Italy
The Allied invasion of Italy began in 1943. Forces Americas Armed Forces played a crucial role in this operation. The invasion started with the landing on Sicily. This event forced Mussolini from power. The campaign continued with battles across the Italian peninsula. The invasion weakened Axis control in Europe.
D-Day and Liberation of Europe
Normandy Landings
The Normandy Landings occurred on June 6, 1944. The Armed Forces Americas launched a massive assault on the French coast. The operation involved land, sea, and air forces. The success of D-Day paved the way for the liberation of France. This event marked a major turning point in the Western theater.
Liberation of Paris
The liberation of Paris followed the Normandy Landings. Allied forces advanced rapidly through France. The city of Paris celebrated freedom in August 1944. The liberation symbolized hope for occupied Europe. The event showcased the strength of the Allied coalition, including the Armed Forces Canada and Armed Forces Middle East.
The War's End and Aftermath
Fall of the Axis Powers
Surrender of Germany
The Allied forces advanced into Germany in 1945. The relentless pressure from the Allies led to the collapse of German defenses. Adolf Hitler's suicide marked a turning point. Germany surrendered on May 7, 1945. This event marked the end of the war in Europe.
Atomic Bombings in Japan
The United States aimed to end the war swiftly. The decision to use atomic bombs targeted Japan. The bombings occurred in Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945. These attacks resulted in massive destruction and loss of life. Japan surrendered on September 2, 1945. The bombings highlighted the devastating power of nuclear weapons.
Post-War Impact
Formation of the United Nations
The world sought to prevent future conflicts. The formation of the United Nations occurred in 1945. The organization aimed to promote international peace and security. Humanitarian issues became a focus. The United Nations included nations like the Northern Ireland United States and others.
Cold War Beginnings
The post-war era saw rising tensions. The emergence of the Cold War shaped global politics. The United States and the Soviet Union became superpowers. Ideological differences fueled the conflict. The Cold War influenced regions like the Island Northern Mariana Islands and Islands Central African Republic.
Historical Examples:
The United Nations played a crucial role in maintaining peace.
The Cold War led to significant geopolitical shifts.
The aftermath of World War II reshaped the world. The creation of the United Nations aimed to prevent another global conflict. The Cold War introduced new challenges and alliances.
World War II reshaped global dynamics and left a profound impact on modern society. The war's aftermath included widespread destruction and significant political changes. The emergence of new global powers altered the world order. Europe experienced substantial economic growth, with GDP per capita tripling in the latter half of the 20th century. The United States emerged as a dominant global superpower, influencing international economic policies. The war also led to increased education and economic prosperity in America, boosting societal confidence. These transformations continue to influence contemporary global relations and economic structures.
See Also
Mapping the World's History Step by Step
Visual History of Warfare: The Ultimate Guide
Exploring and Explaining the World's Great Map Masterpieces
Illustrated History of the Vietnam Conflict: A Comprehensive Overview
Journey Through Time: Ancient Civilizations to the Digital Era

